Comprehending the Diverse Roles of Sugar Cane in Agriculture and Manufacturing
Sugar Cane plays an essential role in both agriculture and manufacturing. As a major money plant, it influences economies in exotic regions. Its adaptability expands beyond sugar production to biofuels and naturally degradable materials. In addition, sugar Cane farming advertises dirt wellness and biodiversity. The complete extent of its payments and possible in lasting techniques continues to be to be discovered. What cutting-edge actions could boost its role in future agricultural systems?
The Agricultural Importance of Sugar Walking Stick
Sugar Cane plays a vital function in agriculture, contributing considerably to the economies of many exotic and subtropical areas. This lawn species thrives in cozy environments, needing sufficient sunshine and water, making it an optimal crop for these areas. Sugar Cane is largely grown for its high sucrose material, which functions as a crucial resources for sugar manufacturing. Furthermore, it plays a significant role in soil preservation by avoiding erosion and boosting soil fertility through its growth cycles. Sugar cane's extensive origin system aids in water retention, profiting surrounding crops. Moreover, the plant supports neighborhood ecological communities by supplying habitat and food for various wild animals species. Farmers usually incorporate sugar Cane right into crop turning systems, improving biodiversity and farming resilience. The farming of sugar Cane not only fulfills local food needs yet additionally fosters lasting farming methods, advertising lasting environmental wellness in farming communities.
Economic Payments of Sugar Cane Farming
Although sugar Cane is frequently neglected, its economic payments are significant, specifically in establishing nations where it functions as an essential money plant. The growing of sugar Cane produces significant revenue for millions of farmers, offering source of incomes and cultivating country growth. As a versatile crop, it sustains different sectors, including sugar production, biofuels, and pharmaceuticals, as a result promoting neighborhood economic situations.
Sugar Cane growing promotes task creation in agricultural industries, processing facilities, and transportation networks. It also adds to international exchange revenues via exports, boosting nationwide financial stability. In regions such as Brazil and India, sugar Cane plays a pivotal role in farming exports, strengthening profession equilibriums.
In addition, the plant's byproducts, like bagasse and molasses, use additional economic opportunities, made use of in power generation and animal feed. The financial effect of sugar Cane expands past simple growing, influencing more comprehensive industrial and farming landscapes.
The Process of Sugar Production From Walking Cane

The journey from sugar Cane to polished sugar includes several crucial stages that highlight the intricacy of sugar manufacturing. Originally, fully grown sugar Cane stalks are harvested and transported to refining facilities. The Cane is after that squashed to draw out juice, which contains a high concentration of sucrose. This juice undergoes information, where impurities are eliminated, frequently making use of lime and warm
Next off, the clarified juice is evaporated to focus the sugar material. The resulting syrup is after that subjected to crystallization, allowing sugar crystals to create. These crystals are separated from the staying syrup via centrifugation and washed to eliminate any type of residual molasses.
The last phase involves refining, where sugar crystals are additional detoxified and bleached, leading to the white granulated sugar commonly utilized in food. This precise process emphasizes the elaborate trip from raw Cane to the sugar that plays an important function in numerous cooking applications.
Sugar Cane as a Resource of Biofuels
As interest in sustainable power resources grows, sugar Cane has arised as a considerable prospect for biofuel manufacturing. The plant's high sugar content enables effective fermentation procedures, transforming sugars right into ethanol. This biofuel functions as a renewable choice to fossil fuels, minimizing greenhouse gas exhausts and advertising power sustainability.
Nations like Brazil have long utilized sugar Cane for ethanol, establishing substantial manufacturing infrastructure that supports both domestic energy needs and international export. The growing of sugar Cane for biofuel has likewise produced economic chances, especially in rural areas, where it generates employment and supports neighborhood farming.
Sugar Cane biofuels Get More Info can be incorporated right into existing fuel systems, making them a useful service for changing away from typical energy resources. As technological developments proceed to boost manufacturing effectiveness, sugar cane's role in biofuel growth is positioned to expand, additionally contributing to global initiatives toward renewable resource fostering.
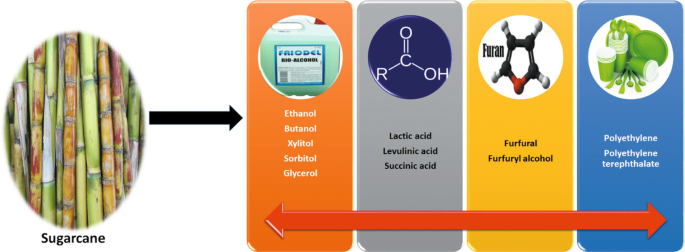
Ingenious Uses of Sugar Cane in Biodegradable Plastics
An expanding number of scientists and suppliers are discovering ingenious uses of sugar Cane in the manufacturing of naturally degradable plastics. Sugar cane, abundant in sucrose, can be processed to create polylactic acid (PLA), a biopolymer that serves as an alternative to petroleum-based plastics. This bioplastic can be used in various applications, consisting of packaging, non reusable cutlery, and farming movies.
Making use of sugar cane-derived PLA provides several benefits, such as lowered reliance on nonrenewable fuel sources and the capacity for reduced carbon exhausts throughout production. Furthermore, sugar walking cane's renewable nature makes it an attractive selection in the quest for sustainable products. Recent developments in handling strategies have improved the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of generating these bioplastics, fostering higher fostering in the industry. As the need for green solutions grows, sugar Cane stands apart as an important source in the shift towards greener production practices.
Environmental Benefits of Sugar Cane Farming
In addition, sugar Cane calls for less water compared to various other crops, making it ideal for farming in deserts. Reliable use of plant residues, such as bagasse, can minimize Click This Link waste and provide renewable resource resources. Sugar Cane farming can facilitate the establishment of agroforestry systems, creating a collaborating relationship in between trees and plants. These practices not just safeguard the setting however additionally promote lasting agricultural techniques, ultimately profiting local areas and communities.
The Future of Sugar Cane in Sustainable Practices

Moreover, the potential for sugar Cane to add to renewable energy sources is getting grip. Biofuels stemmed from sugar Cane can significantly reduce carbon discharges compared to fossil fuels, lining up with global environment objectives. Additionally, developments in waste monitoring permit the use of byproducts, even more reducing environmental impact.
Research right into drought-resistant sugar Cane ranges is likewise underway, providing resilience against environment adjustment. As stakeholders across the industry embrace these lasting methods, sugar Cane is poised to play a vital role in fostering farming sustainability, guaranteeing its importance in future markets and contributing positively to eco-friendly balance.

Regularly Asked Concerns
How Does Sugar Cane Affect Dirt Health and Fertility?
The effect of sugar Cane on soil health and fertility is considerable. Its comprehensive origin system improves soil structure, while raw material from decomposing leaves adds vital nutrients, advertising overall fertility and sustaining diverse microbial life.
What Are the Labor Problems for Sugar Cane Workers?
Labor conditions for sugar Cane employees vary commonly, often defined by lengthy hours, low earnings, and hazardous settings. Many face difficulties such as absence of accessibility to health care and not enough safety steps versus unsafe conditions.
Can Sugar Cane Be Grown in Non-Tropical Climates?
Sugar Cane usually thrives in tropical climates as a result of its warmth and humidity requirements. Particular non-tropical areas might successfully cultivate it through particular agricultural methods, though yields and high quality may be considerably minimized.
What Vermin Frequently Intimidate Sugar Cane Crops?
Parasites harmful sugar Cane plants consist of the sugarcane borer, aphids, and nematodes. These microorganisms can substantially influence plant return, this hyperlink demanding efficient bug administration methods to assure healthy and balanced growth and make the most of agricultural productivity.
Just How Does Sugar Cane Farming Influence Resident Communities?
The growing of sugar Cane significantly impacts local areas by giving work chances, promoting economic development, and affecting social structures. Additionally, it can lead to ecological difficulties, affecting agricultural techniques and neighborhood health in the area.
Sugar Cane is largely cultivated for its high sucrose content, which offers as a vital raw material for sugar production. Farmers usually incorporate sugar Cane into plant rotation systems, improving biodiversity and agricultural durability. The trip from sugar Cane to polished sugar involves numerous essential stages that highlight the complexity of sugar production. The last stage entails refining, where sugar crystals are further detoxified and bleached, resulting in the white granulated sugar generally made use of in food products. The plant's high sugar web content allows effective fermentation processes, transforming sugars into ethanol.